In today’s digital age, computers are essential in our daily routines. Whether we’re browsing the web, working, or enjoying video games, they help us with various activities and tasks.
What Is GPU In Computer? (Short answer)
A computer’s graphics processing unit (GPU) handles the rendering and processing of images and videos. This allows the computer to run demanding tasks like gaming, video editing, and other graphics-heavy applications smoothly.
This article will explain what a GPU is, how it works, and why it’s important in today’s computers, using simple and easy-to-understand language for everyone.
Introduction
A Graphics Processing Unit (GPU) is an essential part of modern computers, playing a major role in tasks like gaming, video editing, and AI projects. But what exactly is a GPU, and why does it matter? Let’s explore its importance and how it contributes to your computer’s performance.
What Is A GPU?
A GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is a specialized processor designed to handle graphics-related tasks. Unlike a CPU (Central Processing Unit), which is optimized for general computing tasks, the GPU is built to handle complex calculations at high speeds, making it ideal for rendering images, videos, and animations.
What Are GPUs Used For?

GPUs are mainly used for rendering graphics in video games, video editing, and graphic design. They are also great at handling multiple tasks simultaneously, making them key for scientific simulations, AI, and even cryptocurrency mining.
History of GPUs
GPUs have evolved significantly since they were first introduced.
- 1980s-1990s: Early graphics cards were simple and only provided basic 2D acceleration.
- 2000s: The rise of dedicated GPUs from NVIDIA and ATI (now AMD) revolutionized gaming and computing.
- 2010s-Present: GPUs are now used for AI, cryptocurrency mining, and scientific research.
How Does A GPU Work?
A GPU uses parallel processing, meaning it can perform thousands of calculations simultaneously. This is why it is far superior to a CPU in handling graphics-intensive tasks. Unlike a CPU, which has fewer cores optimized for sequential processing, a GPU has thousands of smaller cores designed for multitasking.
The Difference Between CPU & GPU
CPUs (central processing units) are designed for general tasks like running programs and managing system operations. In contrast, GPUs are specialized for tasks like rendering 3D graphics and video decoding.
While CPUs have fewer cores with the ability to process complex instructions, GPUs have many cores designed for handling parallel tasks efficiently, such as rendering images or decoding videos.
Types of GPUs
- Integrated GPUs: Built into the CPU, commonly found in laptops and budget desktops.
- Dedicated GPUs: Standalone graphics cards with their own memory (VRAM), offering superior performance.
- External GPUs (eGPUs): Used to boost laptop graphics performance by connecting an external GPU enclosure.
Gpu Vs Cpu: Key Differences
| Feature | GPU | CPU |
| Processing Power | Handles multiple tasks in parallel | Optimized for sequential processing |
| Workload | Best for graphics, AI, and gaming | Best for general computing tasks |
| Energy Consumption | Higher power consumption | More energy-efficient for basic tasks |
GPU and CPU: Working Together
The CPU and GPU work together to handle different tasks in a computer. The CPU manages general tasks like running applications and controlling system functions, while the GPU is specialized for processing graphics and parallel tasks like rendering images, AI, and simulations.
By using both, you can boost overall system performance, as each processor excels at different jobs.
GPUs in the Data Center

In data centers, GPUs play a vital role in handling complex tasks like AI, media analytics, and 3D rendering. Intel’s Xeon processors with integrated graphics and the Intel Data Center GPU Flex and Max Series provide powerful GPU performance.
These GPUs support parallel operations, making them ideal for advanced applications like machine learning, cloud gaming, and content creation.
What Do Gpus Do?
GPUs are powerful chips that handle graphics, gaming, video editing, AI, and more. They speed up tasks like 3D rendering, machine learning, and cryptocurrency mining. With fast memory and special parts, they work quicker than CPUs. Many companies use GPU clusters for AI training, gaming, and virtual reality experiences.
What Is A Cloud GPU?
A cloud GPU is a Graphics Processing Unit hosted on cloud servers, allowing users to access its power remotely. It’s used for tasks like graphics rendering, machine learning, and parallel processing, without needing physical hardware.
How Does GPU Computing Work?
GPU computing works by using the GPU’s ability to process many tasks at the same time. Unlike CPUs, which handle tasks one at a time, GPUs can break down complex problems into smaller tasks that are processed in parallel across multiple cores.
This is especially useful for graphics, simulations, and machine learning. Developers use tools like CUDA or OpenCL to take advantage of GPU power, speeding up computations far beyond what a CPU can do.
Uses of GPU in a Computer
- Gaming: Smooth gameplay, realistic graphics, and ray tracing.
- Video Editing & Rendering: Faster video exports and real-time effects.
- AI & Machine Learning: GPUs accelerate neural network training.
- Cryptocurrency Mining: Solves complex equations for blockchain transactions.
Scientific Computing: Used in simulations, medical research, and space exploration.
Benefits Of Using Gpus
Here’s a simple table showing the benefits of using GPUs:
| Benefit | Description |
| Faster Processing | Reduces time for tasks like gaming, AI, and scientific computing. |
| Energy Efficiency | Uses less power than CPUs while delivering better performance. |
| Better Graphics | Creates realistic visuals for gaming, 3D rendering, and animations. |
| AI & Machine Learning | Speeds up deep learning and data processing tasks. |
| Parallel Processing | Handles multiple tasks at once, improving efficiency. |
Why Are GPUs Important?
GPUs are important because they handle complex graphics and data processing that CPUs can’t manage as efficiently. They enable smooth gameplay, realistic visuals, and fast performance in tasks like video editing, AI, and scientific computing.
With gaming and applications becoming more advanced, a powerful GPU ensures optimal performance in modern devices.
How To Choose The Right GPU?
When selecting a GPU, consider:
- Performance requirements
- VRAM capacity (4GB, 8GB, or more)
- Compatibility with your system
- Budget constraints
Popular GPU Manufacturers
- NVIDIA: Famous for GeForce RTX and AI-focused GPUs.
- AMD: Known for the Radeon series, offering competitive gaming performance.
- Intel: Recently entered the GPU market with the Arc series.
The Future of GPUs

- AI-driven GPUs: Improved performance for deep learning.
- Ray Tracing Advances: More realistic lighting and reflections.
- Better Power Efficiency: New technologies to reduce heat and power consumption.
Common GPU Terms Explained
- CUDA cores: NVIDIA’s processing units for parallel tasks.
- Ray tracing: Simulates light reflections for realistic graphics.
- VRAM: Dedicated memory for storing graphics data.
- Overclocking: Boosting GPU speed for extra performance.
How To Maintain A GPU?
- Regularly clean the GPU to prevent dust buildup.
- Use proper cooling solutions like fans or liquid cooling.
- Keep drivers updated for the best performance.
Common GPU Problems and Troubleshooting
- Overheating: Ensure proper airflow and cooling.
- Driver issues: Keep software updated.
- Performance drops: Check for bottlenecks in CPU or RAM.
Is an expensive GPU always better?
Not necessarily! A high-end GPU is great for professionals, but mid-range options can handle gaming and everyday tasks efficiently without breaking the bank.
Do I Need A GPU?
You need a GPU if you do gaming, video editing, 3D work, or AI tasks. For basic tasks like browsing or watching videos, an integrated GPU is enough. A dedicated GPU boosts performance for heavy tasks, making everything run faster and smoother.
What Is GPU Computing?
GPU computing uses the power of a graphics processing unit (GPU) to perform calculations typically handled by a CPU. It accelerates tasks like scientific simulations, machine learning, and image processing by using the GPU’s ability to process many tasks at once. This speeds up complex calculations, improving performance for data-heavy applications.
What Are The Benefits Of GPU Computing?
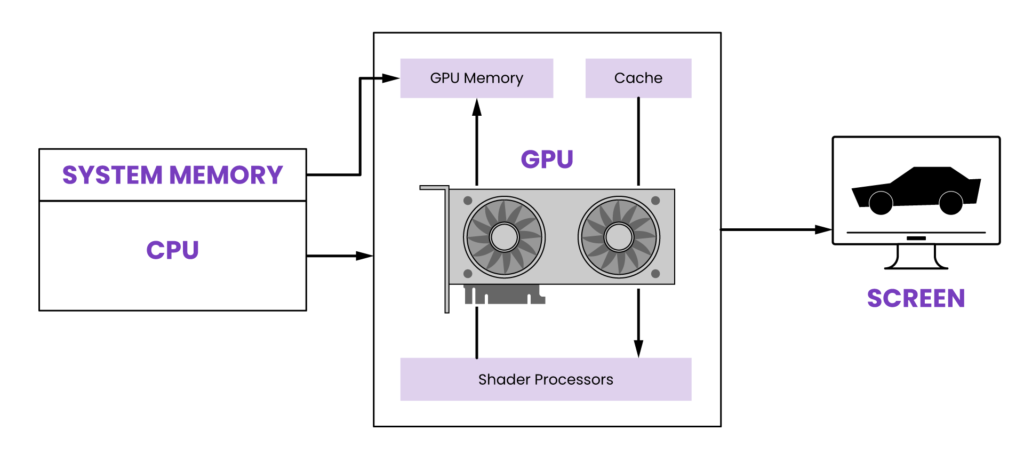
GPU computing provides benefits like faster processing and parallel task handling, making it ideal for graphics rendering, scientific simulations, machine learning, and data analysis. GPUs speed up computations, offering better performance than traditional CPU-based methods.
How Can AWS Help With Your GPU Requirements?
AWS helps with GPU requirements by offering scalable and flexible cloud solutions through Amazon EC2 instances. These instances provide various GPU options, such as P2 for general GPU tasks, P5 for deep learning and HPC, and G5 for cost-efficient graphics workloads.
AWS allows you to rent GPUs for tasks like AI, video editing, and 3D rendering, ensuring optimal performance for any workload.
GPU Price
The price of a GPU can vary widely based on its performance and use case. Entry-level GPUs can cost as low as $100, while high-end models like NVIDIA’s RTX 3090 or specialized AI GPUs can exceed $2,000. Prices fluctuate depending on market demand and availability.
GPU in AI
GPUs are crucial in AI because they can handle parallel processing, making them ideal for training machine learning models. They accelerate tasks like deep learning, neural network computations, and data processing, reducing the time required for AI model training.
GPU Function
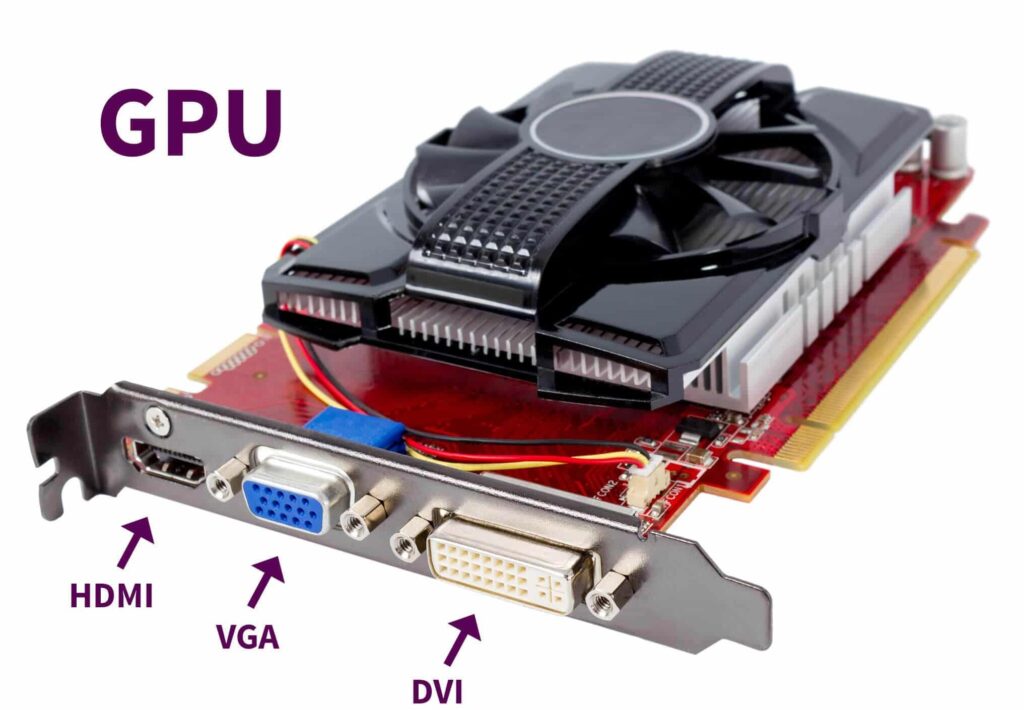
The main function of a GPU is to render graphics and handle complex computations for tasks such as video games, 3D rendering, and image processing. It can also be used for general-purpose computing tasks like AI, simulations, and cryptocurrency mining, thanks to its parallel processing capabilities.
FAQ,s
1. Is GPU a graphics card?
Yes, the GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is the processor on a graphics card. A graphics card includes the GPU along with memory (VRAM), a cooling system, and other components that work together to handle visual tasks.
2. What Is Gpu GPU in a Laptop?
In a laptop, the GPU is a dedicated or integrated processor that handles graphics and visual tasks. It can be part of the CPU (integrated GPU) or a separate component (dedicated GPU), providing the power needed for gaming, video editing, and other graphics-intensive tasks.
3. What Is Gpu GPU in a Computer and How Does It Work?
A GPU in a computer is a specialized processor designed to accelerate the rendering of images, videos, and animations. It works by processing many tasks in parallel, breaking down complex computations into smaller chunks. This allows it to handle graphics-heavy tasks like gaming and video editing more efficiently than a CPU.
4. What Does A GPU Do To A Computer?
A GPU accelerates graphics rendering and handles parallel tasks like gaming, video editing, AI, and 3D rendering, improving overall performance for these tasks.
5. Which Is Better, CPU or GPU?
Both are essential, but for general tasks like running software, the CPU is better. The GPU excels at graphics-intensive tasks, parallel computing, and machine learning.
6. How Much GPU Do I Need?
It depends on your tasks. For casual use, integrated graphics may suffice. For gaming or video editing, a dedicated GPU with more VRAM (4GB or more) is ideal. For professional use like AI or 3D rendering, a high-end GPU is necessary.
7. Is GPU the Same as a Graphics Card?
Yes, the GPU is the processor on a graphics card. The graphics card includes the GPU, memory (VRAM), and other components needed for graphics processing.
8. What Is The Purpose Of A GPU In A Computer?
The GPU is designed to render images, videos, and animations efficiently. It also accelerates parallel tasks like machine learning and scientific simulations, enhancing overall system performance in specific tasks.
9. Could You Explain How GPUs Work?
GPUs process multiple tasks simultaneously by breaking complex problems into smaller chunks. They use thousands of cores to handle many operations at once, which speeds up tasks like graphics rendering, AI, and parallel computing tasks.
10. Are GPUs and Graphics Cards the Same?
No, GPUs and graphics cards are not the same. A GPU is the chip responsible for processing graphics, while a graphics card is the complete hardware that includes the GPU, memory, and other components, all connected to the motherboard to display visuals on a monitor.
11. How do I check my GPU?
- Windows: Press
Win + R, typedxdiag, press Enter. Go to the Display tab to see GPU name and info. - Or press
Ctrl + Shift + Esc, open Task Manager → Performance tab → Click GPU.
12. How do I make sure my GPU is being used?
- Open Task Manager (
Ctrl + Shift + Esc→ Performance tab → Check GPU usage while running a game or app. - Or use MSI Afterburner or GPU-Z to monitor real-time GPU activity.
13. How do I know if my GPU is in place?
- Check if GPU is firmly inserted into the PCIe slot and the power connectors are properly attached.
- Shut down PC and unplug it. Open the case.
Conclusion
To sum up, the GPU is an important part of modern computers, helping with tasks like gaming, video editing, AI, and scientific work. It works alongside the CPU, improving performance. As technology grows, GPUs will keep getting more powerful, so understanding how they work is key to using your computer well.